Type 2 diabetes happens when your body is not able to properly process food as energy. When you have diabetes, your body either does not respond to or does not produce insulin – the hormone that delivers glucose to the body cells. According to doctors, having too much glucose in your bloodstream leads to damage to the blood vessels and nerves that run throughout your body, including to the eyes.
Eyes are sensitive organs that cannot sustain repeated damage to the optic nerve, leading to glaucoma – a condition which may not cause any obvious symptoms so many people do not become aware that they are losing their eyesight unless serious harm gets done. “Usually, the illness gradually reduces a person's field of vision until only the items directly in front of them are visible, a condition known as tunnel vision. Glaucoma might result in irreversible blindness if treatment is not received,” Dr.
Uday Tekchandani, Consultant Ophthalmologist at Dr. Agarwals Eye Hospital, told Times Now. How does diabetes lead to glaucoma? According to Dr.
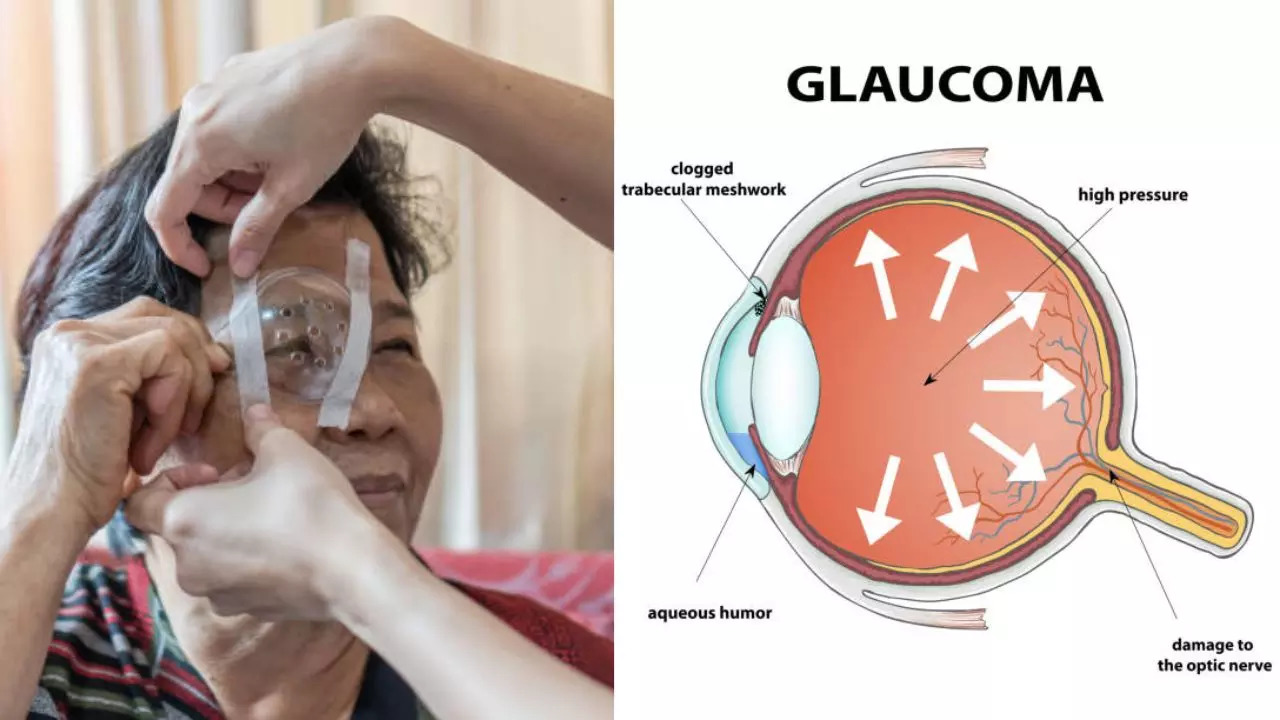
Tekchandani, when the blood vessels in your retina become damaged, they lead to abnormal blood vessels growing in your eye - known as neurovascular glaucoma. These blood vessels block your eye’s natural drainage system, increasing your eye pressure, thereby causing glaucoma. Many studies say diabetic retinopathy increases the risk of glaucoma as high blood sugar causes an increase in a specific glycoprotein known as fibronectin to form in your eye.
Having more fibronectin in your eye may block your eye’s natural drainage system. Key risk factors for glaucoma Dr. Tekchandani has given a few risk factors that lead to glaucoma in diabetic patients, a few of these include: High Eye Pressure Also known as intraocular pressure, it is the primary risk factor for glaucoma.
“When the fluid inside the eye, called aqueous humour, does not drain properly, it can build up, increasing pressure within the eye. This increased pressure can damage the optic nerve,” said Dr. Tekchandani.
Refractive Errors Those who need corrective lenses for vision issues like near-sightedness or farsightedness may be at increased risk. Genetics Dr. Tekchandani said glaucoma also runs in families.
“Although glaucoma is more frequent in adults over 40, it can sometimes strike younger people, especially if there is a family history of the condition,” he said. Age People of all ages can be affected, but the risk rises with age. To check for any indications of glaucoma, those over 40 years of age should undergo routine eye exams.
Lifestyle habits A few lifestyle factors that contribute to the development of glaucoma include: Drinking too much water in the morning Yoga and head-down postures Vigorous exercise Wearing tight collars and ties that restrict blood flow Systemic health conditions like high blood pressure Why Regular Eye Screening is important? According to Dr. Tekchandani, it is important to have regular eye exams which are essential since glaucoma develops without any warning signs, particularly in individuals who are more susceptible. “Even though there is no cure for glaucoma, it can be controlled if diagnosed early.
Treatment typically involves prescription eye drops, oral medications, laser therapy, or surgery, all of which can help control eye pressure and prevent further damage to the optic nerve,” he said. Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world..