Whenever the urge comes, urinating is something we do without giving much thought to it. We almost take it for granted. Interestingly, every time a person urinates, the body is doing some pretty amazing things.
Do you know why you urinate or even what the urine is made of? It will you pay great dividends to know a bit about the way your body works and the role of urine in determining health status. Why we pee At the microscopic level, your body is constantly working to keep you healthy, even while you sleep. Complex chemical processes take place throughout the body, including the breakdown of proteins into molecules known as amino acids.

When your body breaks down amino acids, ammonia is left over as waste. That’s not something you want in your body for long—ammonia is toxic to human cells. Since ammonia is toxic to your body, you need a way to remove it.
That happens partly in the liver, where the ammonia is broken down into the less-toxic chemical, urea. Urea then combines with water and gets flushed into your bladder through the kidneys as urine, protecting your body from its own chemical processes. What is urine made of? In the simplest terms, urine is about 95 percent water and 5 percent urea and other solids.
But urine is much more complex than this simple formula suggests. Urine contains five to 10 times the number of chemical compounds found in other common body fluids like saliva—more than 3,000 different chemical compounds in total. Your pee contains the remnants of the various foods you eat, as well as drug byproducts, bacterial waste, cosmetics, and chemicals found in your environment.
Why study urine? You may be wondering why your doctor asks you to pee in a cup. This test could be ordered to look for signs of a specific disease or condition. But it can also be used to provide general information about your health.
The exact contents of your urine can tell doctors a lot about you. Medical professionals use a diagnostic tool called urinalysis to take a careful look at the chemical makeup of your urine. Urinalysis can reveal warning signs for various diseases and conditions, such as hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), diabetes, kidney stones and many others.
In the following slides, learn more about the clues left in your pee that can tip you off to your urinary health. Bloody pee (Hematuria) Hematuria can make your pee red or pink. If you have blood in your urine, the colour of your pee may change to red, pink, or dark brown like cola.
Doctors call this hematuria, and while it isn’t usually painful, it can be a sign of serious health problems. There are many, many potential causes for blood in the urine. Some of them are moderately serious, while others are life-threatening.
Potential causes of bloody urine include: bladder stones, cancer of the bladder, kidney, or prostate; enlarged prostate (benign prostate hyperplasia, BPH), kidney problems – including kidney stones and kidney disease, medications such as penicillin, aspirin, and cyclophosphamide, which is a cancer treatment; strenuous exercise, particularly running and urinary tract infections (UTIs). Anytime you notice bloody urine, take it seriously. You should contact your doctor right away, as many of the causes are serious.
Sometimes berries can turn your urine red. Urine colour can sometimes be misleading. Sometimes your pee will come out red, but it’s not actually bloody.
Some medicines can make urine red, including the laxative Ex-lax. Certain red foods can stain the colour of your urine too, including rhubarb, beets, and some berries. Most people can’t tell the difference, but your doctor can determine whether your urine looks red because of blood or something else.
Why does pee smell funny? Foods, dehydration, and health problems can all cause urine odour. If your pee smells unusual, there may be several reasons. Vitamins can change the smell of urine, and so can pharmaceuticals.
Certain foods are infamous for making pee smell stronger, such as asparagus, Brussels sprouts, garlic, coffee, and foods with lots of vitamin B-6 such as bananas and salmon. Also, if you aren’t drinking enough water your pee can smell stronger than usual. Serious health problems can also affect the smell of urine.
Infections in the bladder or kidneys, diabetes, and liver failure can all influence the smell. These problems leave a persistent smell, so if your urine changes odour and it stays that way no matter what you eat, tell your doctor. Red Pee and UTIs Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are as painful and irritating as they are common.
They can make your urine look red, brownish-red, or cloudy. UTIs can also change the smell of your pee, and it may burn when you pee if you have one. Many people with UTIs also feel the need to urinate more frequently.
Women are about four times more likely to get UTIs than men. Most UTIs are caused by bacteria. If a UTI is suspected, your doctor may order a leukocyte esterase test.
This method of urinalysis reflects how many white blood cells are in your pee—esterase is an enzyme produced by white blood cells. If you have an infection, esterase may show up in your urine. Your test may also be positive for pus in the urine (pyuria), another sign of infection.
UTIs (including bladder infections) can bring other symptoms as well. Signs of bladder infection include exhaustion, shakiness, fever, back pain, and pressure in the lower abdomen. Tell your doctor if you think you might have a UTI.
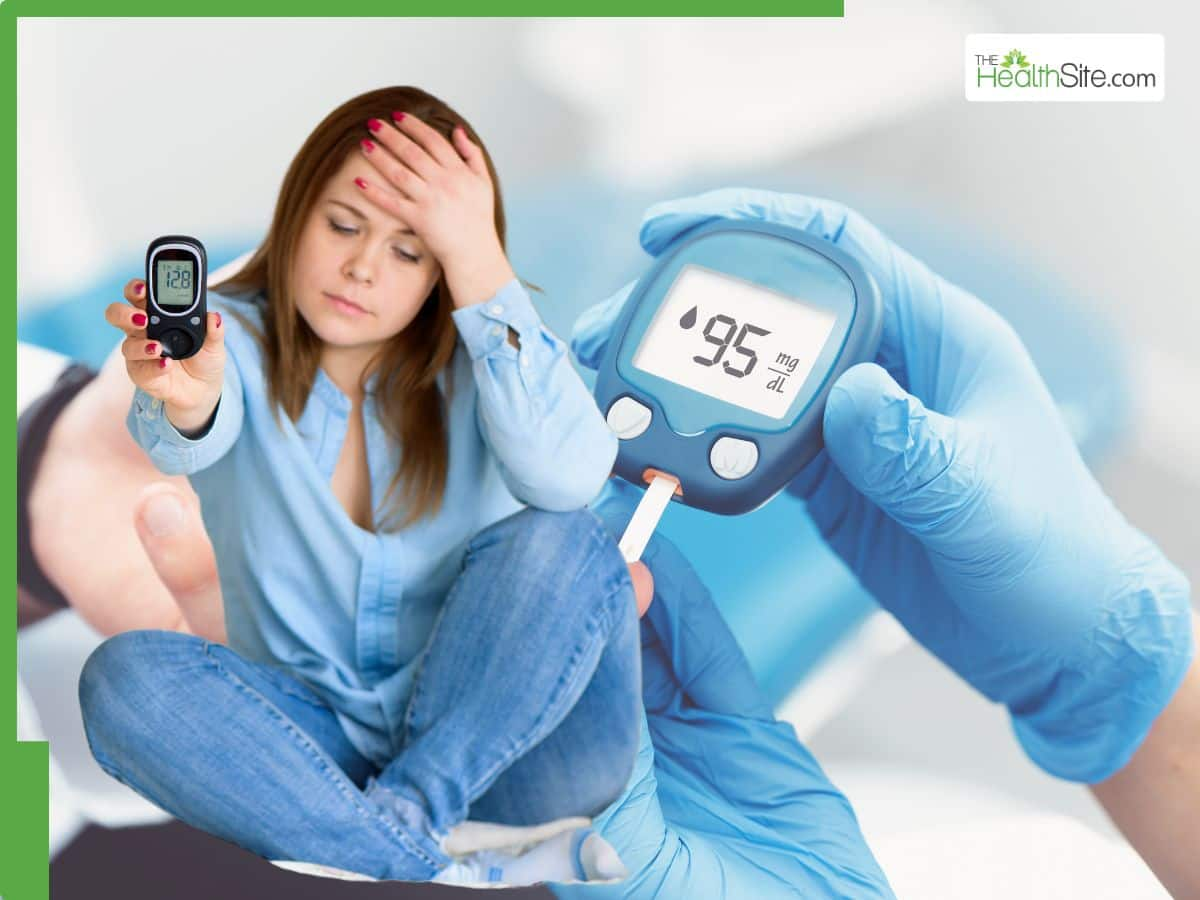
If that’s the cause of your trouble, it can be treated with antibiotics. Your doctor may also prescribe phenazopyridine, a drug that relieves the burning pain and irritation of urinary tract infections. High blood sugar (Hyperglycemia) One of the many chemicals that may appear in urine is glucose, the sugar that fuels your body.
How much glucose is found in your pee can be a clue to your health. That’s because your kidneys start to eliminate glucose through your urine if your blood sugar level is too high. High blood sugar, also called hyperglycemia, is a telltale symptom of diabetes.
While a urine glucose test can be a helpful indicator of hyperglycemia, it is usually performed with additional testing to provide a more reliable result. When your urine tests positive for high glucose, this may be accurate, but it may not. Several factors can throw off a urine glucose test.
For one, the test can only reflect what your blood glucose was a few hours ago. Some medicines including vitamin C can throw off the test as well. And when the test is being evaluated, certain lights can even throw the result off.
For these reasons, you can expect further testing if high levels of glucose are found in your urine. Culled from www.medicinenet.
com.