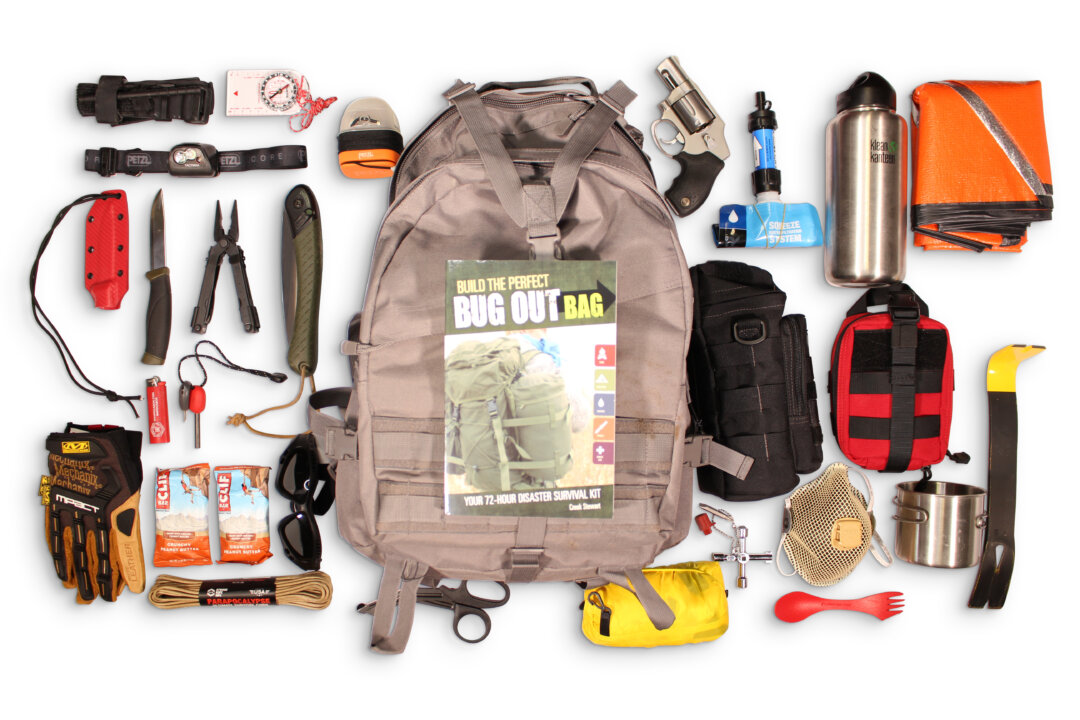
It’s the middle of the night. You wake from a deep sleep and smell smoke. When you come to, you see flames in the next room and realize your house is on fire.
Go bag 72-hour bag Evacuation bag Disaster survival kit Emergency kit Stewart, author of “Build the Perfect Bug-Out Bag,” said he’s learned from survival that the darkest times can provide our greatest resources—physical and psychological. Your bug-out bag should not be too heavy to carry long distances during an emergency. For example, if your car breaks down, or you need to flee on foot because of a forest fire or other natural disaster.
Preparing in advance allows you the time to decide what you'll need to survive in various worst-case scenarios. Without this preparation, you could be scrambling to gather supplies as a storm approaches or during an emergency—when you’re likely to be stressed and overwhelmed. Stewart says there’s no need to make it complicated, and having a bug-out bag tucked away can give you peace of mind.
“It doesn’t have to cost thousands of dollars—it can be really simple, and you get to touch on a lot of different elements of survival,” he said. An evacuation is ordered due to a coming storm—you grab your bag and leave quickly. You wake up to a house fire or a wildfire headed your way.
A robber breaks into your house, and you need to get out fast. A family member is critically injured in an accident, and you need to get to the hospital as soon as possible. A natural disaster forces you from your home, and you and your family spend weeks in a shelter.
Your city is attacked by bombing or a bioweapon. A dam breaks near your community, and you need to leave before your home floods. One of your children falls out of a tree in your yard, and you grab your bag (which contains medical supplies) to help them.
Riots break out near your home, and you want to leave to avoid potential problems. Shelter Water Fire Food First-aid Water (one gallon per person per day) Non-perishable food (several days worth) Flashlight and extra batteries Battery-powered or hand-crank radio First-aid-kit Lighters, matches, and candles kept in containers or resealable bags to keep them dry Medications (at least a 7-day supply) Whistle (to signal for help) Multi-purpose tool, wrench, pliers (to turn off utilities if needed) Tarps or plastic sheeting, scissors, and duct tape (for shelter) Personal sanitation/hygiene items (wet wipes, toilet paper, pads/tampons, garbage bags, plastic ties) Can opener Cell phones and chargers Maps Copies of important documents like driver’s licenses, passports, birth certificates, insurance policies, and medical records/medication lists, sealed in a waterproof, resealable bag (in case of rain or flooding) Blankets A clean change of clothing, including an outer layer, like a rain jacket (in winter, have gloves, hat, scarf, and heavy socks) Comfortable running shoes or hiking boots (as you may need to walk long distances) Backpacking tent big enough for everyone in your household Sleeping bags and sleeping pads Rain gear/poncho Emergency survival blanket (these are pocket-sized) Camping water filter 1-liter metal canteen filled with fresh drinking water 1–2 collapsible plastic water containers Sillcock key (for accessing commercial water spigots) Ferrocerium rod fire starter, disposable lighter, fire tinder Open-and-eat meals (tuna packs, Spam, power bars, beef jerky, and dried snacks) Small camp stove Utensils and serving bowls Bar of soap in a resealable bag Toothbrush and toothpaste Fixed-blade knife Small folding saw Rechargeable headlamp Personal firearms, pepper spray for self-defense Permanent marker Duct tape Entertainment items like a deck of cards or portable games, which are great for kids Each capable adult should have a bug-out bag, and some of the above items don’t need to be included for each person (for example, you only need one tent). Children should only carry lightweight essentials.
Bug-out bags should be reviewed every few months to ensure foods haven’t expired and to swap out clothing for the appropriate season. Stewart suggests taking your fully loaded bag and hiking for several miles to ensure it’s comfortable and not too heavy. Firearms Pepper spray Tasers (shoots two metal prongs into attackers’ skin to deliver an electric charge) Stun guns (require direct contact and deliver a high-voltage shock) If you include firearms, take a training course (or several), have the relevant paperwork, and know the laws in your state for carrying and using firearms.
Stewart advises adding a self-defense tool you are comfortable with to your emergency preparedness plan. This measure enhances your safety and your family’s security in a crisis. Making bags too heavy— Be sure to test your bag with all its contents to ensure you can carry it comfortably.
Forgetting water—r emember, you can only survive three days without it. Not testing your gear —An emergency is not the time you want to be figuring out how to use your camping stove or water filter, so test your gear beforehand. Packing contents for specific scenarios— It’s important to pack for a variety of potential disasters.
Having too many of one type of item —Have a well-rounded bag of items for more resiliency, for instance, don’t pack more weapons than food. Overlooking your feet — You may have to do a lot of walking with a heavy pack in a worst-case scenario, so comfortable shoes and a few pairs of socks are critical. Buying cheap gear —It’s better to buy fewer quality items that you can depend on rather than cheap gear that could fail in an emergency.
Taking things out of your bag to use when camping or hiking —Keep your bug-out bag intact at all times. Borrowing from it for other events could compromise your bag and, ultimately, your resilience in an emergency. Go through any supplies you already have on hand for your bug-out bag, and keep it simple.
Anything you can do preemptively will increase your resilience. Communicate with those in your household about what you would do in an emergency, know the location of your bug-out bags, and where you would meet if you got separated and had to leave your home. Ready.
gov American Red Cross Creek Stewart (author of “Build the Perfect Bug-Out Bag”) The Prepared Bug-Out Bag Academy.