Increased Risk of Chronic Conditions Cardiovascular disease Cancer Diabetes Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) Cataracts Stroke (1.6 times higher risk) Peptic ulcers (1.4 times higher risk) Metabolic syndrome (0.
9 times higher risk) 26 percent higher overall cardiovascular disease risk 20 percent higher heart attack risk 29 percent higher stroke risk 2.8 times higher risk of heart failure 1.8 times higher risk of ischemic heart disease Cardiovascular disease (43 percent higher) Diabetes (104 percent higher) Cardiovascular disease (71 percent) Dementia (99 percent) Diabetes (95 percent) Cancer (128 percent) Regular exercise and a healthy diet can support weight loss and help reduce chronic inflammation, thereby improving overall metabolic function and strengthening immunity.
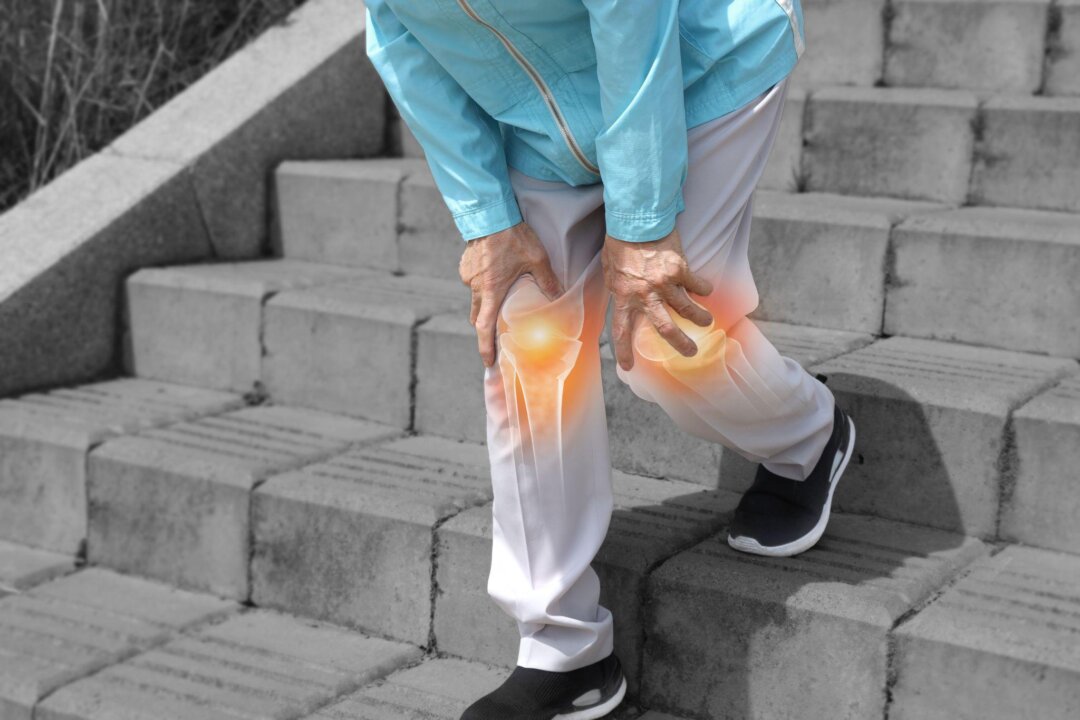
Regular exercise can strengthen the muscles around the joints, reduce joint pressure, and stimulate the secretion of fluid to lubricate the joints, according to Kuo-Pin Wu, superintendent of Taiwan Xinyitang Heart Clinic. Low-impact activities such as walking, swimming, and tai chi are ideal for patients with osteoarthritis, according to Wu. People with osteoarthritis should avoid high-impact or injury-prone movements such as jumping, twisting, and weight training.
It is also important to maintain a steady pace during daily activities and take adequate rest when feeling fatigued to avoid joint damage, according to Wu. Fruits and vegetables: Blueberries, strawberries, tomatoes, bell peppers, and broccoli are rich in antioxidants that help neutralize free radicals in the body. Nuts: Walnuts, pistachios, and almonds are high in dietary fiber and unsaturated fatty acids, offering both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits .
Fish: Salmon, sardines, and tuna are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which provide anti-inflammatory benefits. Whole grains: Whole wheat bread and legumes are rich in dietary fiber, which can aid in weight loss and reduce inflammation , thereby preventing and managing osteoarthritis..