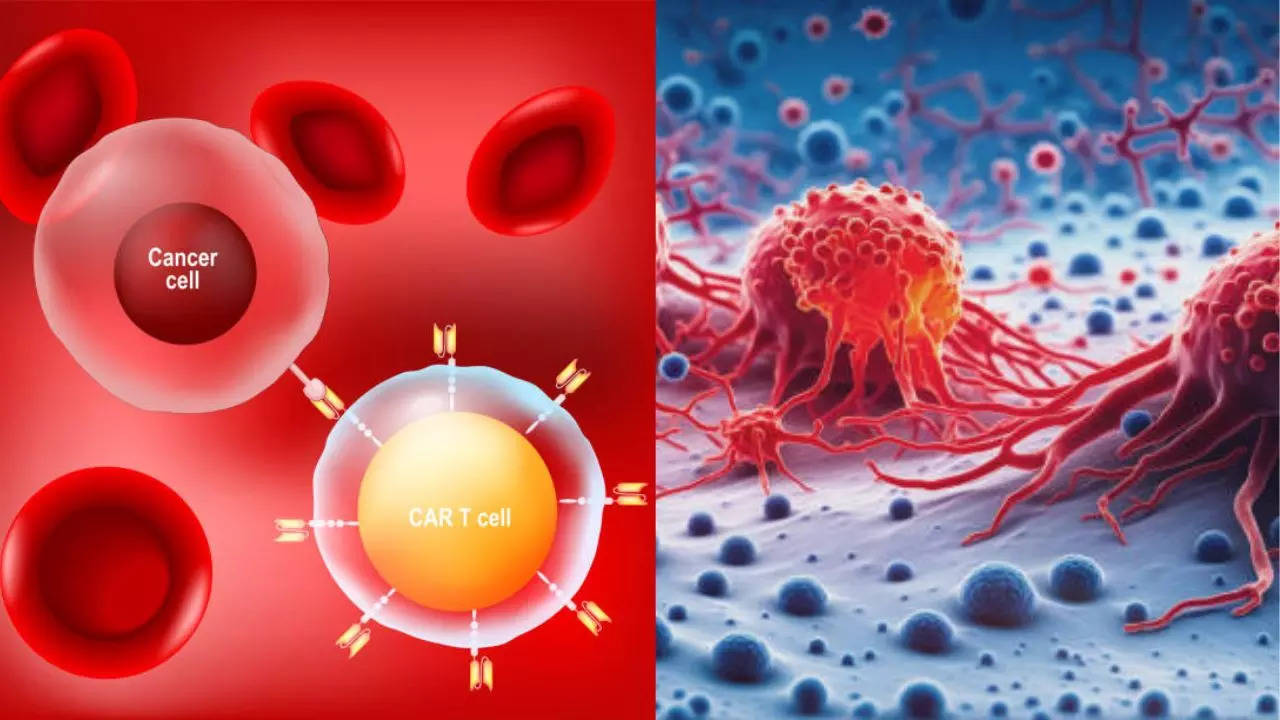
A successful clinical trial at Stanford Medicine has shown that an immune-cell therapy shrank children’s brain tumours, restored neurologic function, and, for one participant, even erased all detectable traces of a brain cancer typically considered incurable. The trial, among the first successes against solid tumours for engineered immune cells known as CAR-T cells - offers hope for children with a group of deadly brain and spinal cord tumours, including a cancer called diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, or DIPG. The findings of the study, published in the journal Nature, have received a regenerative medicine advanced therapy designation from the US Food and Drug Administration, which gives the researchers access to a fast-tracked version of the approval process.
One of the first CAR-T cells successes against tumours This trial has been one of the first successes of CAR-T cells against solid tumours. DIPG, a rare and aggressive brain cancer, has a five-year survival rate of less than 1 per cent, with most patients surviving only about a year after diagnosis. The trial involved 13 participants with either DIPG or similar brain and spinal cord tumours.
Out of 11 who received the treatment, nine showed significant benefits, including improved physical abilities and reduced tumour sizes. However, one patient experienced a complete response – as his tumour disappeared. Four years after his diagnosis, the person remains healthy.
“This disease is usually fatal, but this therapy has shown meaningful tumour reductions and clinical improvements,” said Dr. Michelle Monje, lead researcher of the trial. “While there's still work to be done, this one case gives us hope.
” The treatment was tailored to target GD2 - a marker found in DIPG cells. Even though the therapy did lead to some initial side effects like fever and inflammation, patients showed notable progress. The only person who had a complete response was diagnosed at 16 and now regained many abilities lost to the disease, including walking unassisted.
He is now studying forestry in college. What are CAR-T cells? According to experts, CAR-T cells are engineered from a patient's immune cells to target cancer. Previously successful in blood cancers, this trial tested their effectiveness on solid tumours.
CAR-T cell therapy has revolutionized cancer treatment, achieving significant success in hematological cancers through targeted immunotherapy. However, translating this success to solid tumours has proven challenging due to unique obstacles such as the hostile tumour microenvironment, which induces CAR-T cell dysfunction, and tumour heterogeneity, which complicates effective targeting. Additionally, the physical barriers within solid tumours impede CAR-T cell infiltration, reducing therapeutic efficacy.
While recent clinical trials show promise in treating specific solid tumours, further research is needed to develop innovative approaches to overcome these challenges and enhance the potential of CAR-T cell therapy. Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world..