NEC Corporation is developing a technology that uses AI to analyze the trustworthiness of information on the Internet from multiple perspectives and support fact-checking. This is being carried out as part of a project under Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications to develop and demonstrate technologies to counter false and misleading information on the internet. The effectiveness of the technology will be evaluated by fact-checking organizations such as the Japan Fact-check Center and mass media, including broadcasters, with the aim of improving its trustworthiness.
The demonstration project, which began in August, runs until March 2025. Framework of the new technology The large volume of false and misleading information on the internet has become a growing problem, and countermeasure technologies are attracting greater attention. Fact-checking organizations and media outlets that are responsible for disseminating highly reliable information are burdened by the large amount of labor that is required to determine the trustworthiness of information.

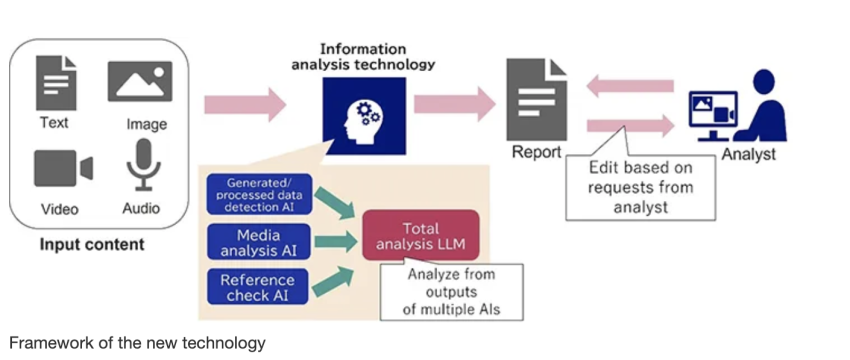
NEC is developing a technology to support fact-checking by utilizing state-of-the-art AI, such Large Language Models (LLM) to analyze and judge the authenticity of content. Outline of the technology The technology uses AI to analyze whether content consisting of multiple types of data (text, images, video, and audio) is false or misleading. First, the technology detects whether images and other data have been processed, AI then recognizes multiple types of data and converts them into text.
Next, LLM that specialize in false information analysis evaluate the text to determine whether the content is correct, whether the information has a reliable source, and whether there are any inconsistencies among the data (e.g., discrepancies between the text and video content).
In addition, the technology creates reports in a format similar to reports and articles prepared by experts at fact-checking organizations. The technology also helps to improve fact-checking operations by enabling adjustments according to a user's instructions, such as deleting unreliable information or adding new information. Fact-checking organizations such as the Japan Fact-check Center and mass media, including broadcasting stations, will be evaluating the performance of the technology, aiming to improve its trustworthiness and for it to be available for practical application in FY2025~2026.
.














