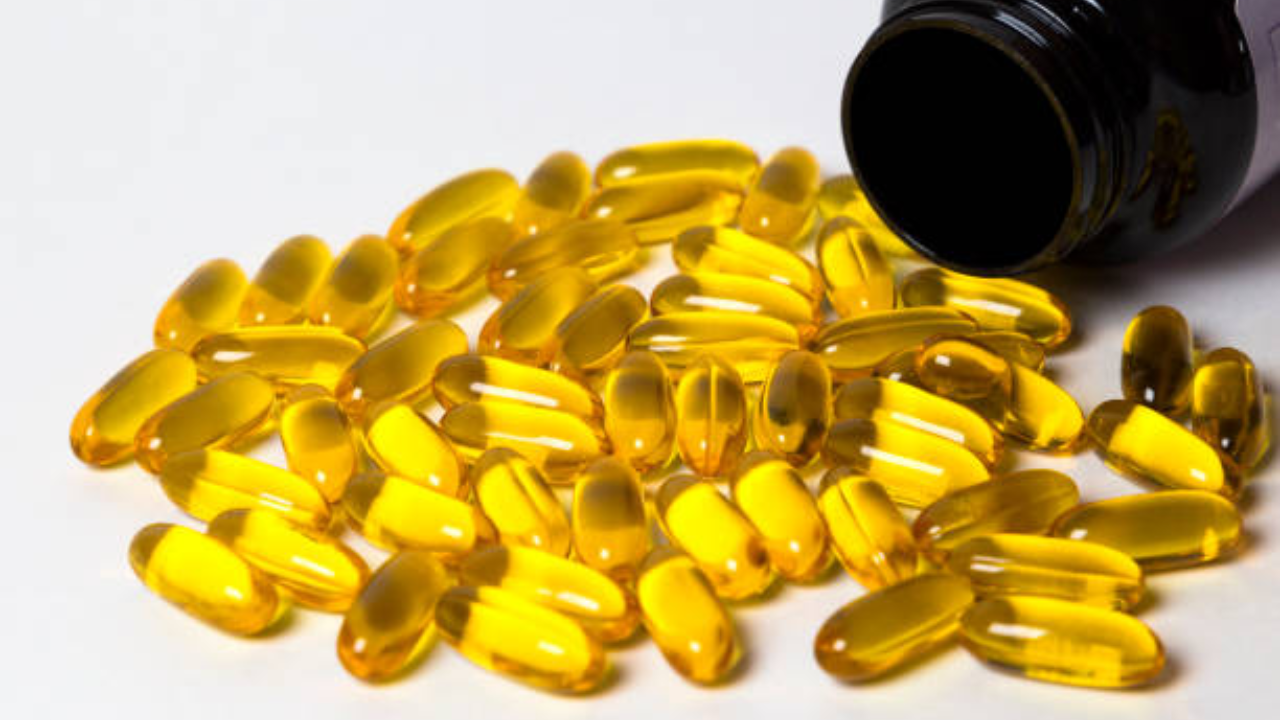
A new study conducted on more than 250,000 people found that a higher consumption of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids can help prevent a variety of cancers. The study was published in the International Journal of Cancer and conducted by researchers from the University of Georgia. Cancer has become a global health concern, especially with increasing early onset.
Omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids are “healthy fats” and important for human health. These are important to the cells and are known to reduce bad cholesterol levels, keep the brain healthy and boost mental health. According to the study, higher levels of omega-3s showed protection against colon, stomach, and lung cancer.
On the other hand, high omega-6 levels protect against brain, malignant melanoma, bladder, and 14 different cancers. Yuchen Zhang, a doctoral student at the University of Georgia’s College of Public Health and lead author said, “Higher omega-3 and omega-6 levels were associated with lower rates of cancer.” Zhang noted that with the significant rise in cancers worldwide, the study “suggests that the average person should focus on getting more of these fatty acids in their diets.
” The researchers analysed data from more than 250,000 people, of which about 30,000 developed some form of cancer in the 10 years of follow-up. Omega-3 and omega-6 are present in fatty fish, nuts, and even some plant oils. However, as diets may not provide the recommended amounts, people often turn to fish oil supplements -- one of the most popular dietary pills on the market.
However, it may not be suitable for all, said the researchers. The study showed that elevated omega-3 levels raised a slightly higher risk of prostate cancer in men. However, the study found no such associations in women.
Instead, they found women and young people to have “stronger beneficial effects of omega-6”. According to a report in IBT, this study’s findings align with historical events where dietary changes have been linked to disease prevention. For instance, the Mediterranean diet, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, has been associated with lower rates of heart disease and certain cancers.
Similarly, the traditional Japanese diet, high in fish and thus omega-3, has been linked to lower rates of heart disease and longer life expectancy. However, it’s important to note that while these findings are promising, they do not suggest that omega-3 and omega-6 supplements should replace a balanced diet or other cancer prevention strategies. It’s also crucial to remember that while these fatty acids have been associated with lower cancer rates, they are not a cure for cancer.
(With inputs from IANS) Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Diet, Health and around the world..