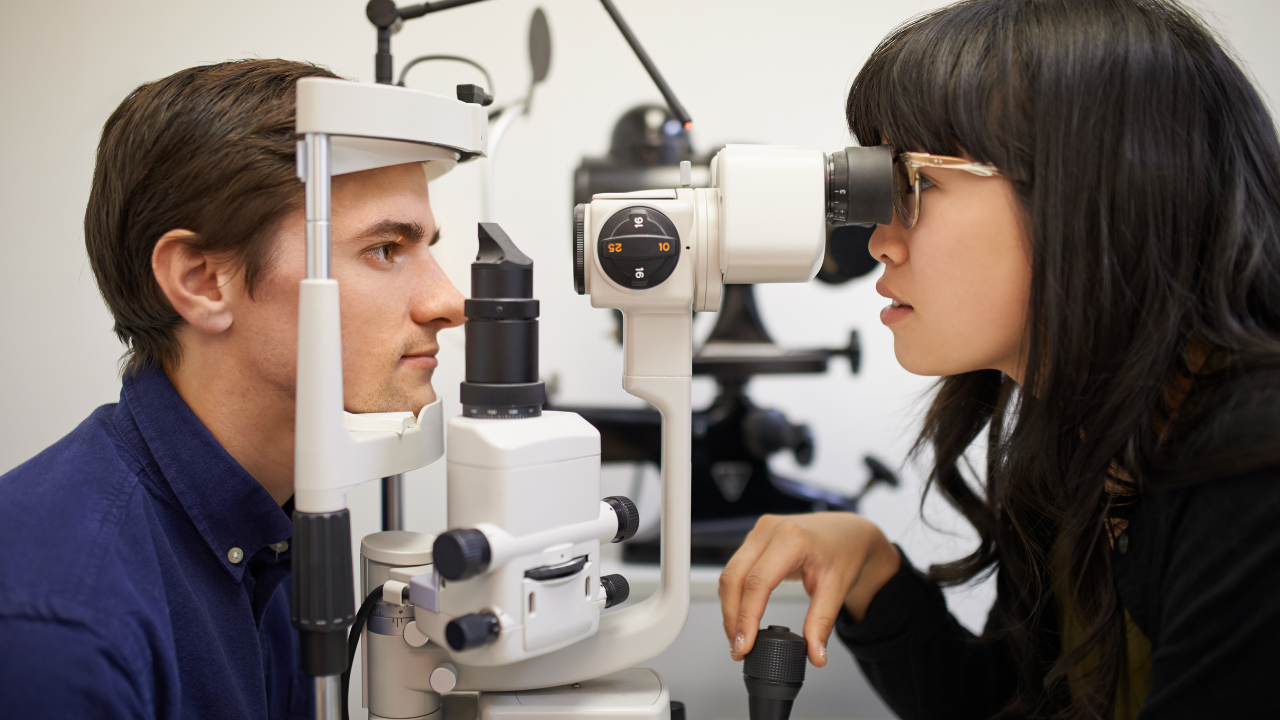
Worldwide, diabetes affects approximately 29.3 million people, with an incidence of diabetic retinopathy at 27%. In India, the figures are equally alarming, with 16.
9% affected. Managing diabetes extends beyond glucose monitoring and medication; it involves vigilant attention to end organ damage that impacts the eyes, kidneys, heart, and brain. Complications from Diabetes in the Eyes “Diabetes can cause a range of complications in the eyes,” says Dr Roshni Mohan, Consultant Ophthalmologist at Dr Agarwals Eye Hospital, Chennai.
“Among these, premature development and progression of cataracts (32%) is common and often requires cataract surgery and intraocular lens implantation.” Another less frequent but significant complication is non-healing corneal ulcers (1.068%), which can necessitate prolonged topical treatments and, in severe cases, keratoplasty.
Despite regular physician visits, many diabetic patients lack awareness about the importance of routine eye check-ups, even in the absence of symptoms. Dr Mohan says, “Diabetic retinopathy is one of the leading causes of blindness, particularly when diabetes coexists with conditions such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and other comorbidities that expedite the progression of retinopathy.” Diabetic Retinopathy and Macular Edema A major cause of vision impairment in diabetic patients is macular edema.
“Patients often report blurry vision, difficulty with near tasks, and glare issues,” says D Mohan. Timely treatment with intravitreal injections can result in significant vision recovery. Diabetic retinopathy is classified into several stages: mild, moderate, severe, and proliferative.
Dr Mohan explains, “The key to managing diabetic retinopathy is maintaining glycemic control. The duration of diabetes and inadequate blood sugar management are primary factors contributing to retinopathy development.” For mild to severe stages, treatment focuses on stringent glycemic control and consistent follow-up appointments, tailored to the stage and presence of macular edema.
Advanced Stages and Vision-Threatening Complications “In cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), treatment options include laser photocoagulation and intravitreal injections,” shares Dr Mohan. Left untreated, PDR can lead to complications such as increased intraocular pressure, redness, and watering, ultimately resulting in neovascular glaucoma (NVG), a painful condition that can lead to irreversible blindness. “Managing NVG requires laser pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), anti-glaucoma medications, and comprehensive eye pressure management,” she adds.
Proliferative retinopathy can also result in vitreous haemorrhage, presenting as floaters. Early intervention with laser treatment is critical, while advanced cases may require vitrectomy surgery. Dr Mohan points out, “If membranes form within the eye (tractional retinal detachment), patients will notice a marked drop in vision, necessitating surgical removal of these membranes.
” The Importance of Early Detection and Preventive Care “The primary aim of treatment is to prevent the onset and progression of diabetic retinopathy,” says Dr Mohan. Regular annual or biannual screenings are essential for early detection, significantly reducing disease burden. “A collaborative approach with tight glycemic control and coordination with a physician can make a substantial difference, especially in the early stages of retinopathy,” she concludes.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world..