A new study has revealed that oxygen deprivation, caused by conditions such as high-altitude hiking and sleep apnea, may be a key factor contributing to the decline in male fertility observed over the past 50 years. Published in Nature Reviews Urology, the review highlights how "testis hypoxia"—a lack of oxygen in the testes—can negatively impact sperm quality and overall reproductive health. Infertility in men is defined as the inability to achieve pregnancy after 12 months of regular, unprotected intercourse, while subfertility refers to a reduced likelihood of conception.
According to lead author Dr Tessa Lord, a reproductive biologist and senior lecturer at The University of Newcastle, Australia, testis hypoxia is a critical factor in declining male fertility. Chronic medical conditions like sleep apnea and varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum) are primary contributors to this condition. “Varicocele is a common abnormality that accounts for infertility in up to 45% of men struggling to conceive,” Dr.

Lord explained. Sleep apnea, another condition linked to testis hypoxia, occurs when throat muscles narrow the airway during sleep, reducing blood oxygen levels. Rising rates of obesity, a major risk factor for sleep apnea, have exacerbated this issue.
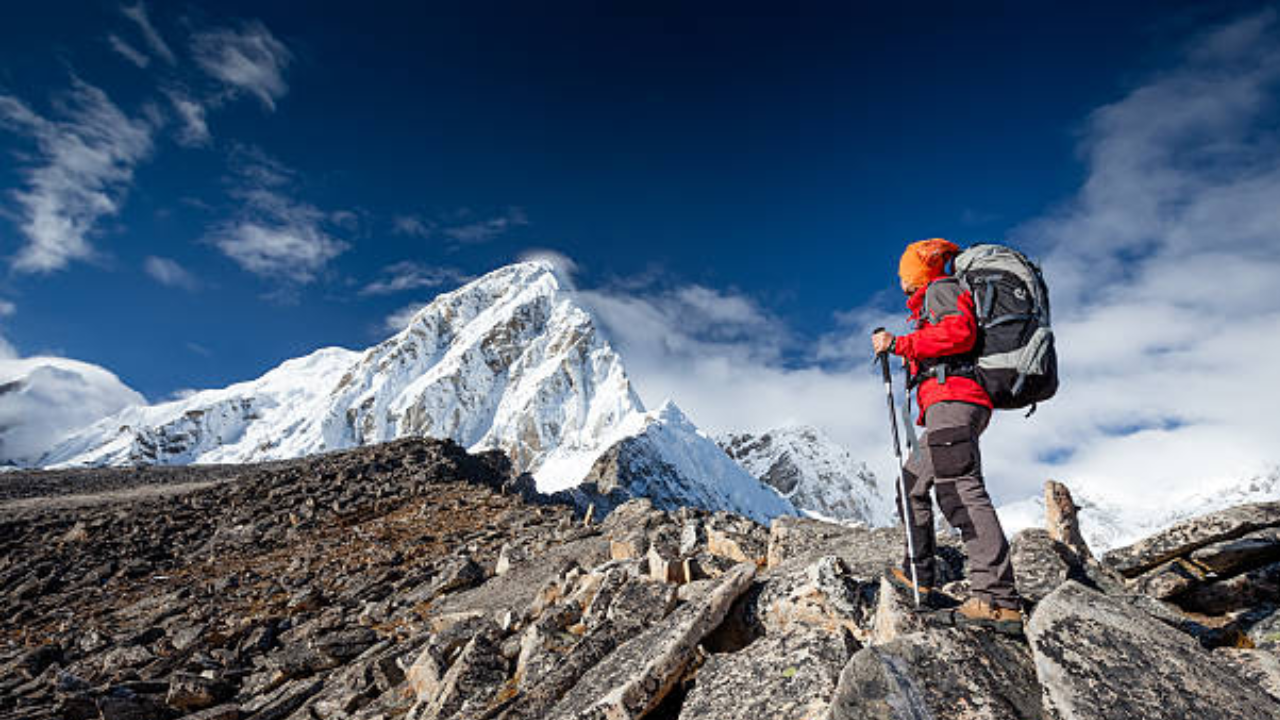
Exposure to high altitudes, where oxygen levels are significantly lower, is also linked to temporary declines in fertility. While hiking in these regions can cause short-term testis hypoxia, the effects may take months to resolve after returning to sea level. Dr.
Lord emphasized that although short-term exposure to hypoxia can affect sperm count and quality, the long-term implications for embryo development and offspring health remain unclear. The study underscores the importance of addressing testis hypoxia as a factor in male infertility, given the significant decline in sperm counts over recent decades. “Emerging evidence suggests that testis hypoxia in fathers could lead to developmental issues in embryos, potentially resulting in fertility problems in the next generation,” Dr.
Lord added. Ways to Naturally Boost Sperm Count After High-Altitude ExposureIf you’ve recently returned from high-altitude environments or are dealing with other oxygen-deprivation conditions, there are natural steps you can take to improve sperm count and quality: Maintain a Balanced Diet: Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts. Zinc-rich foods like pumpkin seeds and oysters, along with folate-rich greens, support sperm production.
Exercise Regularly: Moderate physical activity improves blood circulation, vital for healthy sperm production. Avoid excessive exercise, which can increase oxidative stress. Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake ensures optimal blood flow to the reproductive organs, promoting sperm health.
Get Quality Sleep: Address sleep apnea with medical interventions like CPAP devices or lifestyle changes to improve oxygen levels and reduce testis hypoxia. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: These habits can exacerbate oxidative stress and reduce sperm quality. Manage Stress: High stress levels can disrupt hormone production and affect fertility.
Practices like yoga and meditation can help. Consider Supplements: Supplements containing vitamin C, vitamin D, and Coenzyme Q10 have been shown to improve sperm health. Stay Cool: Avoid excessive heat exposure, such as hot tubs or saunas, which can negatively affect sperm production.
Get Latest News Live on Times Now along with Breaking News and Top Headlines from Health and around the world..