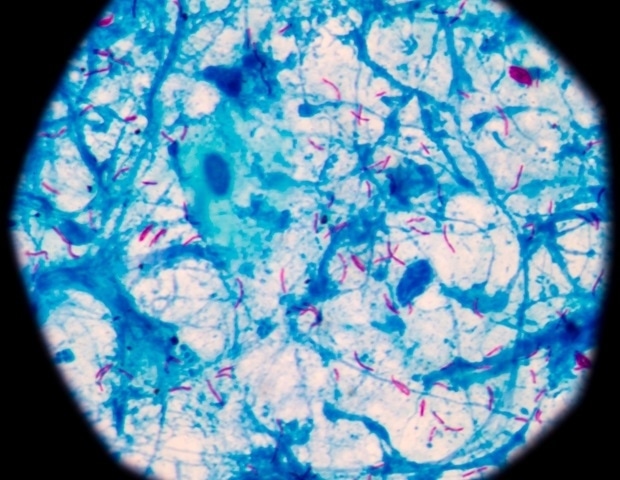
1 2 3 Pune: Of the 2,30,328 cases of tuberculosis the state recorded last year, 36% — or more than 82,000 people — had a more worrying type of TB known as extrapulmonary TB (EPTB), an analysis of state health data has shown. Extrapulmonary TB is defined as tuberculosis that occurs in organ systems other than the lungs, such as lymph nodes, bones and joints and the central nervous systems. Also, it's the drug-resistant forms of TB bacterium that are responsible for most of the EPTB cases in India today, experts have said.
While the global average and national average of EPTB range between 15-20%, Maharashtra's 36% in 2024 is concerning, doctors said. The most common EPTB types are tuberculous lymphadenitis (lymph node TB), skeletal TB (bone and joint TB), and genitourinary TB, which impacts the urinary tract or the genital organs. Diagnosing EPTB cases is also a challenge as it doesn't have the same symptoms as TB.

In fact, to detect EPTB, one would need invasive procedures such as a biopsy to retrieve samples or imaging systems that are not always available at all levels of healthcare. EPTB patients are generally not infectious unless they also develop pulmonary TB, but if left undiagnosed mortality rates can be high. Another challenge is incorrect diagnosis, doctors said.
"Many times, I saw oncologists referring patients to me after they removed a tumour and only after a biopsy did we know it was actually a TB case," said Dr Mahavir Modi, a city-based pulmonologist, adding that in some other cases, a non-TB tumour was treated with tuberculosis drugs. Dr Modi added: "Symptoms in EPTB are not related to the classically known TB symptoms like coughing, weight loss or fever. So for an inexperienced doctor, TB may not be the first diagnosis.
EPTB is a challenge for public health because it's not infectious, but can lead to deaths if left undetected and untreated. A TB culture test is also a must to ensure whether it is a routine TB case or an MDR-TB one because the line of treatment would depend on drug-resistance of the TB." Dr Sandeep Sangale, joint director (TB and leprosy) of the state public health department, said despite the challenges in diagnosis, health workers were able to identify over 82,000 EPTB cases in 2024.
Dr Sangale said: "It is a challenge. For example, stomach pain as a symptom is not commonly associated with TB. So doctors would have to conduct tests to rule out other illnesses and then arrive at possible abdominal TB.
Symptoms for the most commonly detected EPTB, lymph node TB, include swollen glands over the neck region. But since this is not painful, the symptom often ends up ignored by patients." Get the latest lifestyle updates on Times of India, along with Navratri Wishes , Eid Messages and quotes !.